### 어파인(아핀) 변환과 투시 변환, 리매핑
#### 어파인 변환 vs 투시 변환
- 어파인 변환 : affine transform
- 투시 변환 : perspective transform, projective transform, homography transform
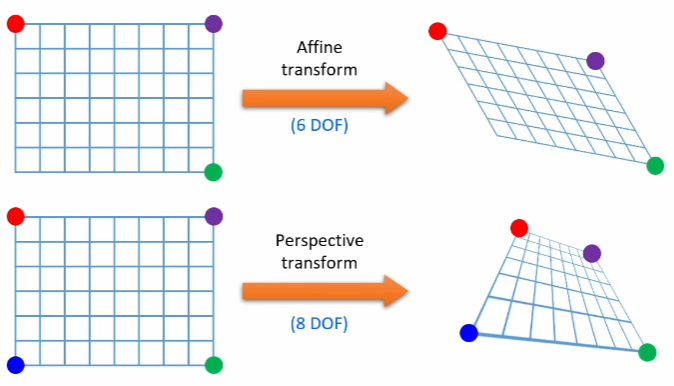
 - 빨강점, 보라점, 초록점 각각 2개씩 총 6개의 미지수로 구성되어있는 Affine transform 매트리스를 계산
- 빨강점, 보라점, 초록점, 파랑점 각각 2개씩 총 8개의 미지수로 구성되어있는 Perspective transform 매트리스를 계산
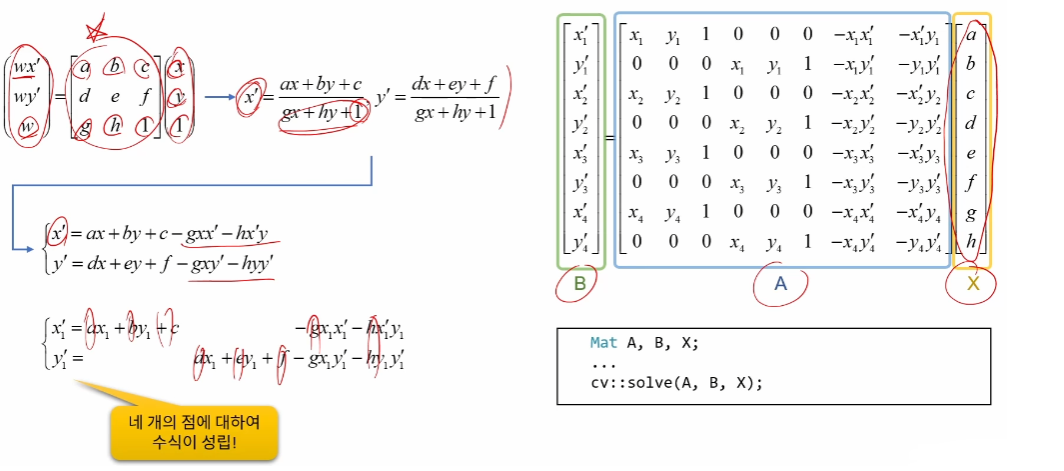
#### 어파인 변환 행렬 구하기
- 3 점의 이동 결과를 알고 있을 때 사용
```
Mat getAffineTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[]);
Mat getAffineTransform(InputArray src, InputArray dst);
```
- src : 3개의 원본 좌표점 (Point2fsrc[3]; 또는 vectorsrc;)
- dst : 3개의 결과 좌표점 (Point2fdst[3]; 또는 vectordst;)
- 반환값 : 2 x 3 크기의 변환 행렬
#### 투시 변환 행렬 구하기
- 4 점의 이동 결과를 알고 있을 때 사용
```
Mat getPerspectiveTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[], int SolveMethod = DECMOP_LU);
Mat getPerspectiveTransform(InputArray src[], InputArray dst, int SolveMethod = DECMOP_LU);
```
- src : 4개의 원본 좌표점 (Point2fsrc[4]; 또는 vectorsrc;)
- dst : 4개의 결과 좌표점 (Point2fdst[4]; 또는 vectordst;)
- 반환값 : 3 x 3 크기의 변환 행렬(CV_64F)
- 4개의 대응점으로부터 투시 변환 행렬 구하기
#### 영상의 어파인 변환
```
void warpAffine(InputArray src, OutPutArray dst, InputArray M, Size dsize, int flags = INTER_LINEAR, int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
```
- src : 입력 영상
- dst : 출력 영상(src와 같은 타입)
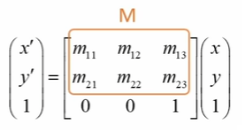
- M : **2 x 3** 어파인 변환 행렬 (CV_32F or CV_64F)
- dsize : 결과 영상의 크기
- flags : 보간법 선택
- borderMode : 가장자리 픽셀 처리 방식
- boderValue : boderMode가 BORDER_CONSTANT 일 경우 사용할 픽셀 값
#### 영상의 투시 변환
```
void warpPerspective(InputArray src, OutPutArray dst, InputArray M, Size dsize, int flags = INTER_LINEAR, int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
```
- src : 입력 영상
- dst : 출력 영상(src와 같은 타입)
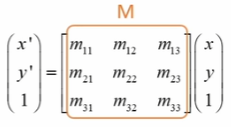
- M : **3 x 3** 어파인 변환 행렬 (CV_32F or CV_64F)
- dsize : 결과 영상의 크기
- flags : 보간법 선택
- borderMode : 가장자리 픽셀 처리 방식
- boderValue : boderMode가 BORDER_CONSTANT 일 경우 사용할 픽셀 값
```
#include
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
Mat src = imread("lenna.bmp", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (src.empty()) {
cerr << "Image load failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat trans = (Mat_(2, 3) << 0.5, 0, 100, 0, 0.5, 100);
// 100, 100 만큼 이동함과 동시에 가로, 세로 scale 값을 0.5를 줌으로써 가로, 세로 1/2만큼 축소된 형태
Mat dst;
warpAffine(src, dst, trans, Size(700, 700));
imshow("src", src);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey();
}
```
- 빨강점, 보라점, 초록점 각각 2개씩 총 6개의 미지수로 구성되어있는 Affine transform 매트리스를 계산
- 빨강점, 보라점, 초록점, 파랑점 각각 2개씩 총 8개의 미지수로 구성되어있는 Perspective transform 매트리스를 계산

#### 어파인 변환 행렬 구하기
- 3 점의 이동 결과를 알고 있을 때 사용
```
Mat getAffineTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[]);
Mat getAffineTransform(InputArray src, InputArray dst);
```
- src : 3개의 원본 좌표점 (Point2fsrc[3]; 또는 vectorsrc;)
- dst : 3개의 결과 좌표점 (Point2fdst[3]; 또는 vectordst;)
- 반환값 : 2 x 3 크기의 변환 행렬
#### 투시 변환 행렬 구하기
- 4 점의 이동 결과를 알고 있을 때 사용
```
Mat getPerspectiveTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[], int SolveMethod = DECMOP_LU);
Mat getPerspectiveTransform(InputArray src[], InputArray dst, int SolveMethod = DECMOP_LU);
```
- src : 4개의 원본 좌표점 (Point2fsrc[4]; 또는 vectorsrc;)
- dst : 4개의 결과 좌표점 (Point2fdst[4]; 또는 vectordst;)
- 반환값 : 3 x 3 크기의 변환 행렬(CV_64F)
- 4개의 대응점으로부터 투시 변환 행렬 구하기

#### 영상의 어파인 변환
```
void warpAffine(InputArray src, OutPutArray dst, InputArray M, Size dsize, int flags = INTER_LINEAR, int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
```
- src : 입력 영상
- dst : 출력 영상(src와 같은 타입)
- M : **2 x 3** 어파인 변환 행렬 (CV_32F or CV_64F)
- dsize : 결과 영상의 크기
- flags : 보간법 선택
- borderMode : 가장자리 픽셀 처리 방식
- boderValue : boderMode가 BORDER_CONSTANT 일 경우 사용할 픽셀 값

#### 영상의 투시 변환
```
void warpPerspective(InputArray src, OutPutArray dst, InputArray M, Size dsize, int flags = INTER_LINEAR, int borderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
```
- src : 입력 영상
- dst : 출력 영상(src와 같은 타입)
- M : **3 x 3** 어파인 변환 행렬 (CV_32F or CV_64F)
- dsize : 결과 영상의 크기
- flags : 보간법 선택
- borderMode : 가장자리 픽셀 처리 방식
- boderValue : boderMode가 BORDER_CONSTANT 일 경우 사용할 픽셀 값

```
#include
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
Mat src = imread("lenna.bmp", IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (src.empty()) {
cerr << "Image load failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat trans = (Mat_(2, 3) << 0.5, 0, 100, 0, 0.5, 100);
// 100, 100 만큼 이동함과 동시에 가로, 세로 scale 값을 0.5를 줌으로써 가로, 세로 1/2만큼 축소된 형태
Mat dst;
warpAffine(src, dst, trans, Size(700, 700));
imshow("src", src);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey();
}
```
 #### 버드 아이 뷰(Bird's Eye View)
- 새가 하늘에서 내려다 보듯이, 매우 높은 곳에 위치한 카메라가 아래의 피사체를 찍은 화면
- 투시 변환을 이용하여 전면에서 촬영된 영상을 버드 아이 뷰 처럼 변환할 수 있음
```
#include
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
VideoCapture cap("test_video.mp4");
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
cerr << "Video open failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat src;
while (true) { // 무한 루프를 돌면서
cap >> src; // cap의 매 프레임을 src 객체에 저장
if (src.empty())
break;
int w = 500, h = 260;
vector src_pts(4);
vector dst_pts(4);
src_pts[0] = Point2f(474, 400); src_pts[1] = Point2f(710, 400); // 현재 차선의 앞 사다리꼴 2점
src_pts[2] = Point2f(866, 530); src_pts[3] = Point2f(366, 530); // 현재 차선의 뒤 사다리꼴 2점
dst_pts[0] = Point2f(0, 0); dst_pts[1] = Point2f(w - 1, 0); // 출력 영상의 좌측 상단점의 좌표,
dst_pts[2] = Point2f(w - 1, h - 1); dst_pts[3] = Point2f(0, h - 1);
Mat per_mat = getPerspectiveTransform(src_pts, dst_pts);
Mat dst;
warpPerspective(src, dst, per_mat, Size(w, h));
#if 1
vector pts;
for (auto pt : src_pts) {
pts.push_back(Point(pt.x, pt.y));
}
polylines(src, pts, true, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, LINE_AA); // 라인의 색은 빨강색으로 그림 LINE_AA 방법으로 그림
#endif
imshow("src", src);
imshow("dst", dst);
if (waitKey(10) == 27)
break;
}
}
```
#### 버드 아이 뷰(Bird's Eye View)
- 새가 하늘에서 내려다 보듯이, 매우 높은 곳에 위치한 카메라가 아래의 피사체를 찍은 화면
- 투시 변환을 이용하여 전면에서 촬영된 영상을 버드 아이 뷰 처럼 변환할 수 있음
```
#include
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
VideoCapture cap("test_video.mp4");
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
cerr << "Video open failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat src;
while (true) { // 무한 루프를 돌면서
cap >> src; // cap의 매 프레임을 src 객체에 저장
if (src.empty())
break;
int w = 500, h = 260;
vector src_pts(4);
vector dst_pts(4);
src_pts[0] = Point2f(474, 400); src_pts[1] = Point2f(710, 400); // 현재 차선의 앞 사다리꼴 2점
src_pts[2] = Point2f(866, 530); src_pts[3] = Point2f(366, 530); // 현재 차선의 뒤 사다리꼴 2점
dst_pts[0] = Point2f(0, 0); dst_pts[1] = Point2f(w - 1, 0); // 출력 영상의 좌측 상단점의 좌표,
dst_pts[2] = Point2f(w - 1, h - 1); dst_pts[3] = Point2f(0, h - 1);
Mat per_mat = getPerspectiveTransform(src_pts, dst_pts);
Mat dst;
warpPerspective(src, dst, per_mat, Size(w, h));
#if 1
vector pts;
for (auto pt : src_pts) {
pts.push_back(Point(pt.x, pt.y));
}
polylines(src, pts, true, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, LINE_AA); // 라인의 색은 빨강색으로 그림 LINE_AA 방법으로 그림
#endif
imshow("src", src);
imshow("dst", dst);
if (waitKey(10) == 27)
break;
}
}
```
 ### 리매핑
- 영상의 특정 위치 픽셀을 다른 위치에 재배치하는 일반적인 프로세스

- 어파인 변환, 투시 변환을 포함한 다양한 변환을 리매핑으로 표현 가능

#### 리매핑 함수
```
void remap(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, InputArray map1, InputArray map2, int interpolation, int boderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
```
- src : 입력 영상
- dst : 출력 영상
- map1 : 결과 영상의 각 픽셀이 참조할 입력 영상의 (x,y) 좌표또는 x 좌표를 담고 있는 행렬(CV_16SC2 or CV_32FC2 or CV_32FC1)
- map2 : 결과 영상의 (x,y) 좌표가 참조할 입력 영상의 y 좌표를 담고 있는 행렬(CV_16UC1 or CV_32FC1)
- interpolation : 보간법
- borderMode : 가장자리 픽셀 확장 방식
- borderValue : Border_CONSTANT일 때 사용할 상수 값
```
int main()
{
Mat src = imread("tekapo.bmp");
if (src.empty()) {
cerr << "Image laod failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
int w = src.cols;
int h = src.rows;
Mat map1 = Mat::zeros(h*2, w*2, CV_32FC1);
Mat map2 = Mat::zeros(h*2, w*2, CV_32FC1);
for (int y = 0; y < h*2; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < w*2; x++) {
map1.at(y, x) = (float)x/2;
map2.at(y, x) = (float)y/2;
// map2.at(y, x) = (float)y;
//map2.at(y, x) = (float)h - 1 - y; // 상하 대칭
//map2.at(y, x) = (float)y + 10 * sin(x /32.f); // 물결 모양
}
}
Mat dst;
remap(src, dst, map1, map2, INTER_LINEAR);
//remap(src, dst, map1, map2, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_DEFAULT);
imshow("src", src);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey();
}
```
### 리매핑
- 영상의 특정 위치 픽셀을 다른 위치에 재배치하는 일반적인 프로세스

- 어파인 변환, 투시 변환을 포함한 다양한 변환을 리매핑으로 표현 가능

#### 리매핑 함수
```
void remap(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, InputArray map1, InputArray map2, int interpolation, int boderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
```
- src : 입력 영상
- dst : 출력 영상
- map1 : 결과 영상의 각 픽셀이 참조할 입력 영상의 (x,y) 좌표또는 x 좌표를 담고 있는 행렬(CV_16SC2 or CV_32FC2 or CV_32FC1)
- map2 : 결과 영상의 (x,y) 좌표가 참조할 입력 영상의 y 좌표를 담고 있는 행렬(CV_16UC1 or CV_32FC1)
- interpolation : 보간법
- borderMode : 가장자리 픽셀 확장 방식
- borderValue : Border_CONSTANT일 때 사용할 상수 값
```
int main()
{
Mat src = imread("tekapo.bmp");
if (src.empty()) {
cerr << "Image laod failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
int w = src.cols;
int h = src.rows;
Mat map1 = Mat::zeros(h*2, w*2, CV_32FC1);
Mat map2 = Mat::zeros(h*2, w*2, CV_32FC1);
for (int y = 0; y < h*2; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < w*2; x++) {
map1.at(y, x) = (float)x/2;
map2.at(y, x) = (float)y/2;
// map2.at(y, x) = (float)y;
//map2.at(y, x) = (float)h - 1 - y; // 상하 대칭
//map2.at(y, x) = (float)y + 10 * sin(x /32.f); // 물결 모양
}
}
Mat dst;
remap(src, dst, map1, map2, INTER_LINEAR);
//remap(src, dst, map1, map2, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_DEFAULT);
imshow("src", src);
imshow("dst", dst);
waitKey();
}
```



 - 빨강점, 보라점, 초록점 각각 2개씩 총 6개의 미지수로 구성되어있는 Affine transform 매트리스를 계산
- 빨강점, 보라점, 초록점, 파랑점 각각 2개씩 총 8개의 미지수로 구성되어있는 Perspective transform 매트리스를 계산

#### 어파인 변환 행렬 구하기
- 3 점의 이동 결과를 알고 있을 때 사용
```
Mat getAffineTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[]);
Mat getAffineTransform(InputArray src, InputArray dst);
```
- src : 3개의 원본 좌표점 (Point2fsrc[3]; 또는 vector
- 빨강점, 보라점, 초록점 각각 2개씩 총 6개의 미지수로 구성되어있는 Affine transform 매트리스를 계산
- 빨강점, 보라점, 초록점, 파랑점 각각 2개씩 총 8개의 미지수로 구성되어있는 Perspective transform 매트리스를 계산

#### 어파인 변환 행렬 구하기
- 3 점의 이동 결과를 알고 있을 때 사용
```
Mat getAffineTransform(const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[]);
Mat getAffineTransform(InputArray src, InputArray dst);
```
- src : 3개의 원본 좌표점 (Point2fsrc[3]; 또는 vector #### 버드 아이 뷰(Bird's Eye View)
- 새가 하늘에서 내려다 보듯이, 매우 높은 곳에 위치한 카메라가 아래의 피사체를 찍은 화면
- 투시 변환을 이용하여 전면에서 촬영된 영상을 버드 아이 뷰 처럼 변환할 수 있음
```
#include
#### 버드 아이 뷰(Bird's Eye View)
- 새가 하늘에서 내려다 보듯이, 매우 높은 곳에 위치한 카메라가 아래의 피사체를 찍은 화면
- 투시 변환을 이용하여 전면에서 촬영된 영상을 버드 아이 뷰 처럼 변환할 수 있음
```
#include  ### 리매핑
- 영상의 특정 위치 픽셀을 다른 위치에 재배치하는 일반적인 프로세스

- 어파인 변환, 투시 변환을 포함한 다양한 변환을 리매핑으로 표현 가능

#### 리매핑 함수
```
void remap(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, InputArray map1, InputArray map2, int interpolation, int boderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
```
- src : 입력 영상
- dst : 출력 영상
- map1 : 결과 영상의 각 픽셀이 참조할 입력 영상의 (x,y) 좌표또는 x 좌표를 담고 있는 행렬(CV_16SC2 or CV_32FC2 or CV_32FC1)
- map2 : 결과 영상의 (x,y) 좌표가 참조할 입력 영상의 y 좌표를 담고 있는 행렬(CV_16UC1 or CV_32FC1)
- interpolation : 보간법
- borderMode : 가장자리 픽셀 확장 방식
- borderValue : Border_CONSTANT일 때 사용할 상수 값
```
int main()
{
Mat src = imread("tekapo.bmp");
if (src.empty()) {
cerr << "Image laod failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
int w = src.cols;
int h = src.rows;
Mat map1 = Mat::zeros(h*2, w*2, CV_32FC1);
Mat map2 = Mat::zeros(h*2, w*2, CV_32FC1);
for (int y = 0; y < h*2; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < w*2; x++) {
map1.at
### 리매핑
- 영상의 특정 위치 픽셀을 다른 위치에 재배치하는 일반적인 프로세스

- 어파인 변환, 투시 변환을 포함한 다양한 변환을 리매핑으로 표현 가능

#### 리매핑 함수
```
void remap(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, InputArray map1, InputArray map2, int interpolation, int boderMode = BORDER_CONSTANT, const Scalar& borderValue = Scalar());
```
- src : 입력 영상
- dst : 출력 영상
- map1 : 결과 영상의 각 픽셀이 참조할 입력 영상의 (x,y) 좌표또는 x 좌표를 담고 있는 행렬(CV_16SC2 or CV_32FC2 or CV_32FC1)
- map2 : 결과 영상의 (x,y) 좌표가 참조할 입력 영상의 y 좌표를 담고 있는 행렬(CV_16UC1 or CV_32FC1)
- interpolation : 보간법
- borderMode : 가장자리 픽셀 확장 방식
- borderValue : Border_CONSTANT일 때 사용할 상수 값
```
int main()
{
Mat src = imread("tekapo.bmp");
if (src.empty()) {
cerr << "Image laod failed!" << endl;
return -1;
}
int w = src.cols;
int h = src.rows;
Mat map1 = Mat::zeros(h*2, w*2, CV_32FC1);
Mat map2 = Mat::zeros(h*2, w*2, CV_32FC1);
for (int y = 0; y < h*2; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < w*2; x++) {
map1.at

